Planning is everything in business. But what happens when unexpected expenses come up, and your prepared budget doesn’t leave room to adjust?
A well-prepared budget serves as a financial roadmap, outlining business goals for a fixed period.
You’ve got a meticulously crafted budget, a financial masterpiece. But sometimes, changes in market conditions, supply chain disruptions, or surprise costs can make even the best plans feel inflexible.
That’s where forecasting saves the day for businesses. Unlike budgeting, forecasting is dynamic, adjusting to real-time data and unexpected changes. Together, they form a complete financial planning approach essential for success.
So this blog covers a budget vs forecast comparison, helping you understand them individually.
What is budgeting?
Budgeting is when businesses create a detailed financial plan that aligns a company’s financial resources and activities with its strategic goals and objectives over a specific period. It serves as a roadmap to allocate resources, monitor performance, and guide decision-making to ensure financial stability and growth.
If you want your business to thrive, budgeting isn’t optional. Here’s what a solid budget includes:
- Revenue and expense projections
- Cash flow estimates
- Operational and production costs
- Working capital needs
- Capital expenditures
What is financial forecasting?
Financial forecasting is a forward-looking approach that combines past data, market trends, and the latest data to anticipate financial outcomes. It helps businesses with financial planning and preparation for risks, opportunities, and challenges.
A complete financial forecast should include:
- Reviewing past results and aligning them with current realities.
- Identifying macroeconomic risks, such as pandemics, wars, or significant market changes.
- Preparing best-case and worst-case scenarios for future revenue and costs
- Accounting for surprise expenses like cyberattacks, natural disasters, or system failures.
- Connecting the forecast to your strategic planning and business needs.
Uncertainty is the only certainty in business, but accurate financial forecasting provides the clarity you need to make informed decisions.
Budgeting vs. forecasting: key differences
Alright, we’ve got budgeting and financial forecasting down. Let’s understand how forecasts differ from budgets.
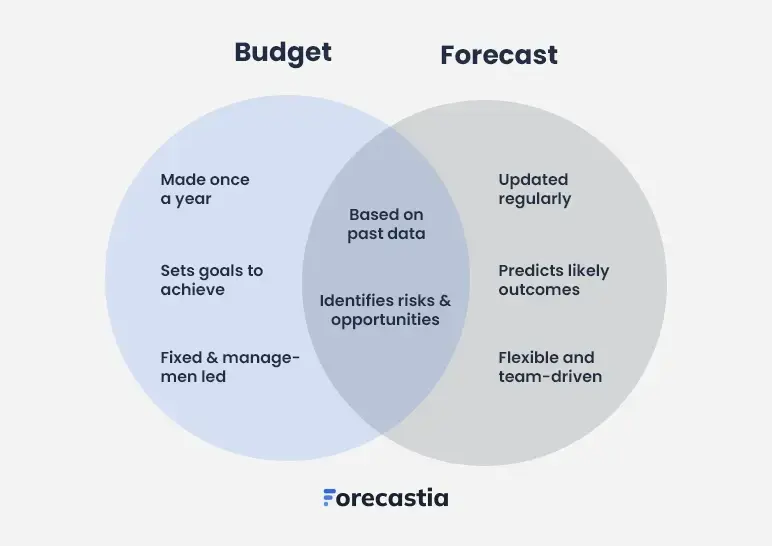
Purpose
Budgeting ensures financial discipline by allocating resources, managing spending, and setting firm limits to keep finances on track.
Forecasting complements budgeting by predicting future outcomes using past data and trends. Updated regularly, it helps businesses adapt to market changes and unexpected events while staying aligned with financial goals.
Together, they create a balanced financial strategy, ensuring both stability and flexibility in business planning
Time frame
Budgets help businesses plan spending over a set period, usually a fiscal year. Fixed from the start, they provide structure and predictability but aren’t updated frequently.
Example: The hiring budget for next quarter is capped at $50K.
Forecasts offer flexibility by adjusting to current data, market trends, and emerging insights. They evolve over months or years, providing a dynamic view of financial performance.
Example: Based on current sales, we expect $500K in revenue this quarter.
Regularly updated forecasts help businesses evaluate scenarios, adapt quickly, and allocate resources effectively.
Level of detail
Budgeting is granular. It organizes revenues, expenses, and resources into firm spending limits, helping businesses maintain control and stability.
However, in a fast-changing environment, detail isn’t always enough.
Forecasting prioritizes adaptability over precision, focusing on broader trends rather than details. Using historical data and market trends, it provides flexible insights, helping businesses navigate sudden changes and make informed decisions in a fast-evolving environment.
Flexibility
Budgeting is all about creating a clear plan for your finances over a specific period, typically a year. Once it’s set, it stays as-is and becomes the standard to measure how well things are going. While it may seem rigid, that’s intentional—it’s designed to provide structure, keep things organized, and ensure accountability throughout the set period.
Financial forecasting is primarily focused on agility, designed to stay relevant by being updated frequently—usually on a monthly or quarterly basis. Using current and past data, as well as scenario analysis, forecasts adapt to economic conditions and evolving market trends with the help of advanced financial forecast models for better accuracy.
This helps businesses align with their financial performance goals and respond effectively to unexpected challenges or opportunities.
Application
Budgets are invaluable for setting clear financial goals, assessing business performance, and ensuring everyone stays within the lines (no overspending allowed). When used effectively, they align teams, optimize resources, and keep everything running like a well-oiled machine.
Forecasting, though, is the navigator for when things get unpredictable. It uses historical data and real-time insights to predict future revenue and spot market trends, helping businesses be prepared to handle economic conditions and stay one step ahead of surprises.
You know the key differences between budget and forecast. Great! But how do they work in real life? To really get a feel for how they work, let’s explore forecast vs budget examples.
Budgeting vs. forecasting examples in financial planning
Whether your company’s size is big or small, combining budgeting and financial forecasting is the smartest way to plan. Let’s break it down with a practical example.
Budget example
Picture a boutique bakery that generated $1.5 million in revenue last year and aims to grow its planned revenue by 20%, targeting $1.8 million. To achieve this, the finance team creates a budget based on market research and allocates resources to key areas like marketing, raw materials, and operations.
This budget outlines spending limits and projected growth, such as a 20% increase in retail sales driven by targeted advertising and product expansion. It helps the bakery manage cash flow effectively while staying financially stable.
Budget for the year
| Category | Previous year actual | Current year budgeted | Actual results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue | $1.5M | $1.8M | |
| Revenue from retail sales | $1.0M | $1.2M | |
| Revenue from catering | $0.5M | $0.6M | |
| Operating expenses | $1.1M | $1.4M | |
| - Marketing | $0.3M | $0.4M | |
| - Raw materials | $0.5M | $0.6M | |
| - Overhead costs | $0.4M | $0.4M | |
| Cash flow (operating income) | $0.3M | $0.4M |
At year-end, the actual results column will reveal whether these targets were met, letting the business owners and the finance team assess performance and adjust plans for the business’s future.
Forecast Example
Let’s consider the same boutique bakery with a revenue target of $1.8M and uses budget forecasting to track growth. By analyzing historical data and performing scenario planning, they identify a steady 2% monthly growth rate and adjust forecasts based on actual performance.
Projected monthly revenue based on 2% growth:
| Month | Projected revenue |
|---|---|
| January | $150,000 |
| February | $153,000 |
| March | $156,060 |
| April | $159,181 |
| May | $162,365 |
| June | $165,612 |
| July | $168,924 |
| August | $172,302 |
| September | $175,748 |
| October | $179,263 |
| November | $182,849 |
| December | $186,506 |
| Total | $1.93M |
This flexibility helps businesses adapt to seasonal demand and unexpected costs by:
- Increasing catering during holidays
- Adjusting marketing if growth slows
- Allocating resources for debt reduction
If March and April sales grow by 3% instead of 2%, the bakery can update forecasts to reflect this momentum, ensuring accurate financial planning.
Budget versus forecast: What do you need the most?
Managing finances is no small feat—markets can shift faster than your morning coffee gets cold.
That’s why you need both—budget and forecast.
Budget = Structure
A budget is your financial blueprint. It sets firm spending limits, ensures resources are allocated efficiently, and helps achieve goals like reducing debt or boosting savings. Think of it as the disciplined backbone of your financial strategy.
Forecast = Flexibility
A forecast, on the other hand, is your crystal ball. It adapts to external factors like market shifts or unexpected opportunities, helping you make informed, timely decisions. It’s not just about reacting to change but planning for the long term—whether it’s performance-based compensation, scaling operations, or aligning revenue with evolving goals.
Together, budgeting and financial forecasting work to track progress, optimize resources, and keep businesses stable—even in uncertain times.
For small businesses, starting with a forecast ensures agility and informed decisions, while combining both over time balances flexibility and stability.
Tips for more accurate budgeting & forecasting
Understanding budgeting and forecasting is one thing, but making them accurate is where the real work begins. Without reliable numbers, even the best plans can fall flat.
Hence here are some helpful tips:
1. Set goals you can actually achieve
The first rule to follow when you create budgets is to be realistic. Use past data and cost analysis to create goals that make sense. Sure, doubling your revenue in six months sounds great, but unless you’ve discovered a magic formula, it’s not happening.
A strong budget also supports priorities beyond growth, like improving cash flow, resolving balance sheet issues, or focusing on debt reduction. With realistic expectations, your budget becomes an important part of your monetary planning for real, measurable success.
2. Build a safety net with a contingency fund
An uncertain business landscape can hit hard, but a contingency fund softens the blow. Calculate your monthly expenses and set aside at least two months’ worth. It’s non-negotiable.
This fund keeps operations running when cash flow decides to play hide-and-seek. With accessible reserves, it’ll be business as usual for you. Sure, unexpected challenges might come, but at least you’ll be ready to meet them head-on without breaking a sweat.
For example, Tesla prioritizes maintaining strong cash reserves, allowing them to reinvest in R&D while staying prepared for potential downturns. Their ability to forecast accurately helps them maintain liquidity even during turbulent market phases.
3. Stay flexible with changing conditions
We’ve to admit that rigid budgeting and forecasting don’t stand a chance in today’s constantly shifting business conditions. Flexibility ensures you can adjust to whatever comes your way.
Stop relying on outdated numbers. They’re just setting you up for bad decisions. Instead, use real-time scenarios and data to make informed decisions. A flexible budgeting and forecasting process means fewer surprises, better accuracy, and more time spent running your business, not putting out fires.
4. Replace spreadsheets with tools
Sure, spreadsheets may be familiar, but they have limits. Manual inputs and fragmented workbooks lead to costly errors.
A financial forecasting tool is a wiser choice like Forecastia, a dedicated financial forecasting software that provides businesses with precise projections.
Accessible and efficient, it doesn’t require a master’s or bachelor’s degree to operate. Forecastia simplifies creating precise, tailored projections and its accessible design ensures businesses can focus on decision-making with ease.
5. Adjust your forecasts regularly
Monitor your budget like your favorite subscription service—regularly. Compare actual results to your forecast vs budget comparison to see how things are shaping up.
When external factors or unexpected events arise, update your forecasts to match the new business conditions. Small businesses benefit from milestones that keep everything on track. Proactive adjustments mean you’re always ready to pivot, making your quantitative forecasting process as dynamic as your business.
Strengthen your business with effective planning
No one ever said running a business would be easy. Budgets keep things stable, while forecasts help you plan for opportunities and risks. Together, they form your financial toolkit for better decision-making.
And if you’re wondering how to make it less painful, the answer is simple: Forecastia. It makes forecasting easier by combining advanced AI with user-friendly tools.
With integrations for platforms like QuickBooks, it generates real-time projections, supports scenario analysis, and provides visual dashboards. This helps businesses adapt to market changes and plan effectively without the usual hassle of spreadsheets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What tool can be used for budgeting and financial forecasting?
Budgeting and forecasting tools include Excel for simplicity, forecasting software for precision, and Enterprise Resource Planning(ERP) systems for seamless integration and scalability.
Can a financial forecasting tool be used for both budget and forecasts?
Yes, it can, but not fully. Only some parts of budgeting can be indirectly managed using a financial forecasting tool. These tools excel in forecasting, offering dynamic insights for long-term planning and adapting to changing business conditions. However, they can assist with certain budgeting aspects too.
What is the main difference between budgeting and forecasting?
A forecast provides a big-picture view of your business’s goals and the external factors influencing them, offering adaptability to changing conditions. A budget, on the contrary, is a detailed, step-by-step financial plan outlining expected revenue, expenses, and resource distribution over a specific period, focusing on stability and control.
Can financial forecasting replace budgeting?
No, financial forecasting can’t fully replace budgeting. Forecasting predicts outcomes and adapts to changes, while budgeting ensures discipline and resource allocation. Both are essential.

